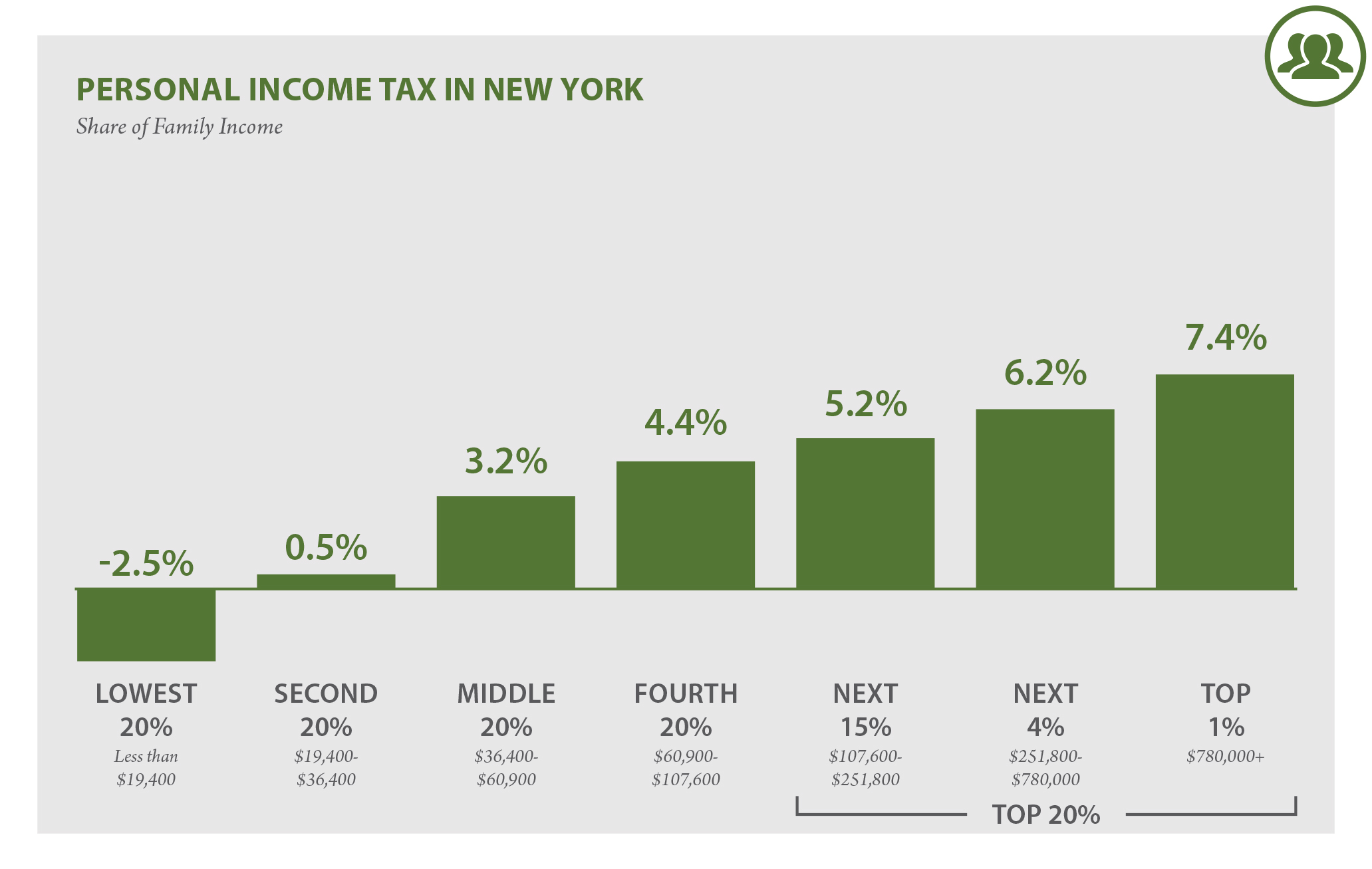
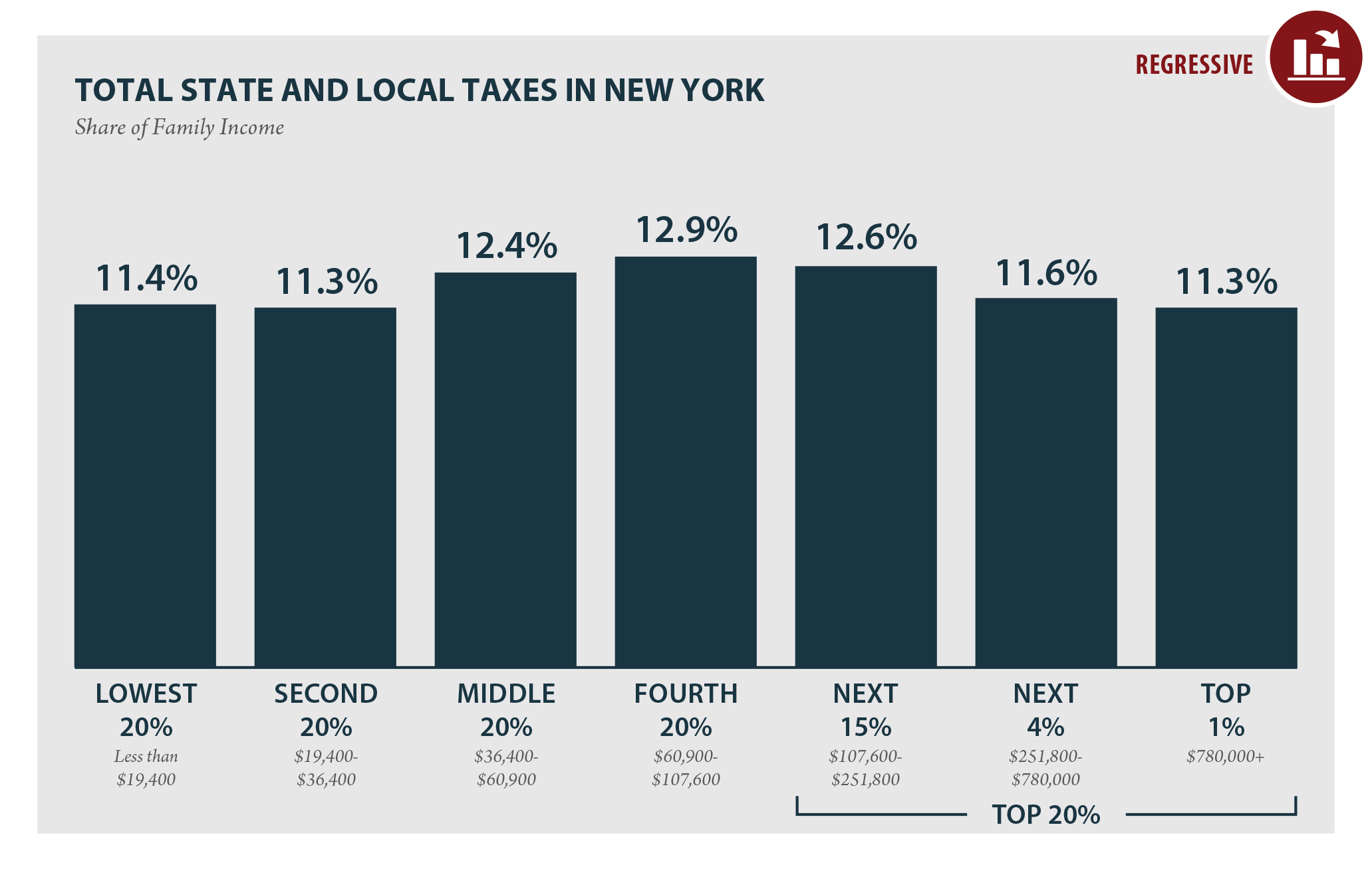
New York State is known for its robust tax structure, and understanding the income tax rate is crucial for residents and businesses alike. The state's income tax system is designed to generate revenue that supports public services, infrastructure, and community programs. As of 2023, the tax rates vary depending on an individual's income bracket, making it essential for taxpayers to stay informed. Whether you're filing taxes for the first time or looking to optimize your financial planning, knowing the intricacies of the New York State income tax rate can help you make smarter decisions.
For many residents, navigating the complexities of state taxes can be challenging. The New York State income tax rate is progressive, meaning higher earners are taxed at higher percentages. This structure ensures that everyone contributes fairly based on their financial situation. Additionally, various deductions, credits, and exemptions are available to help reduce taxable income, making it important for taxpayers to understand their options. Staying updated on the latest tax laws and regulations is key to ensuring compliance and maximizing savings.
As tax laws continue to evolve, it's crucial to remain informed about changes that could impact your financial obligations. Whether you're a resident, business owner, or simply curious about how the system works, understanding the New York State income tax rate is vital. This guide will break down the rates, brackets, and key considerations, helping you navigate the tax landscape with confidence. Let's dive into the details and uncover everything you need to know about the state's income tax structure.
Read also:Discovering Eva Notty Real Name Biography And More
What is the New York State Income Tax Rate?
The New York State income tax rate refers to the percentage of income that residents are required to pay to the state government. This tax is calculated based on a progressive system, where higher income levels are taxed at progressively higher rates. For example, individuals earning below a certain threshold may pay a lower percentage, while those in higher brackets face increased rates. This structure ensures that the tax burden is distributed equitably across different income levels.
How Does the Progressive Tax System Work?
A progressive tax system means that as your income increases, so does the percentage of tax you owe. In New York, the income tax rate is divided into several brackets, each with its own rate. For instance, if you earn $50,000 annually, a portion of your income might be taxed at 4%, while another portion could be taxed at 6%. Understanding these brackets is essential for accurate tax calculations and planning. Additionally, factors such as marital status and dependents can influence your tax obligations.
What is the New York State Income Tax Rate for Different Brackets?
New York State has specific income tax brackets that determine how much tax you owe. As of 2023, the rates range from 4% for lower-income individuals to over 8% for higher earners. Here's a breakdown of the brackets:
- 4% for income up to $8,500
- 4.5% for income between $8,501 and $11,700
- 5.25% for income between $11,701 and $23,200
- 5.97% for income between $23,201 and $215,400
- 6.33% for income between $215,401 and $1,077,550
- 8.82% for income above $1,077,551
Why is Understanding the New York State Income Tax Rate Important?
Knowing the New York State income tax rate is crucial for effective financial planning. Whether you're budgeting for personal expenses, saving for retirement, or managing business finances, understanding your tax obligations ensures you're prepared for the year ahead. Additionally, being aware of deductions and credits can help you reduce your taxable income, potentially saving you money. Staying informed about changes in tax laws is equally important, as these can impact your overall financial strategy.
What are the Key Factors Affecting New York State Income Tax?
Several factors influence the New York State income tax rate, including filing status, deductions, and exemptions. For example, married couples filing jointly may have different tax obligations compared to single filers. Additionally, certain deductions, such as mortgage interest and charitable contributions, can lower your taxable income. Understanding these factors is essential for optimizing your tax return and minimizing your liability.
What is the New York State Income Tax Rate for Businesses?
Businesses operating in New York State are also subject to income tax, with rates varying depending on the type of entity. Corporations, partnerships, and sole proprietorships each have unique tax obligations. For instance, corporations may pay a flat rate on their net income, while partnerships and sole proprietorships pass through income to the owners, who then pay individual income tax. Understanding these differences is critical for businesses looking to comply with state regulations.
Read also:Kate Middleton In Sunglasses A Royal Style Icon
How Can You Reduce Your New York State Income Tax?
There are several strategies to reduce your New York State income tax liability. First, take advantage of available deductions and credits, such as the dependent care credit or education credits. Additionally, contributing to retirement accounts like a 401(k) or IRA can lower your taxable income. Consulting with a tax professional or accountant can provide personalized advice tailored to your financial situation, ensuring you maximize your savings.
What is the New York State Income Tax Rate for Non-Residents?
Non-residents who earn income in New York State are also required to pay taxes on that income. The rate is generally the same as for residents, but non-residents may not qualify for certain deductions or credits. It's important for non-residents to understand their obligations and file the appropriate forms to avoid penalties or interest. Keeping accurate records of income earned in the state is key to ensuring compliance with tax laws.
Table of Contents
- What is the New York State Income Tax Rate?
- How Does the Progressive Tax System Work?
- What is the New York State Income Tax Rate for Different Brackets?
- Why is Understanding the New York State Income Tax Rate Important?
- What are the Key Factors Affecting New York State Income Tax?
- What is the New York State Income Tax Rate for Businesses?
- How Can You Reduce Your New York State Income Tax?
- What is the New York State Income Tax Rate for Non-Residents?
- How Do Deductions and Credits Impact Taxable Income?
- What Should You Know About Filing Taxes in New York State?
How Do Deductions and Credits Impact Taxable Income?
Deductions and credits play a significant role in reducing taxable income in New York State. Standard deductions are available to all taxpayers, while itemized deductions allow you to claim specific expenses, such as medical bills or property taxes. Credits, on the other hand, directly reduce the amount of tax you owe. Examples include the child tax credit and the earned income tax credit. By leveraging these tools, you can significantly lower your tax burden.
What Should You Know About Filing Taxes in New York State?
Filing taxes in New York State requires careful attention to detail and adherence to deadlines. Taxpayers must submit their returns by April 15th each year, unless an extension is granted. Using tax software or working with a professional can simplify the process and ensure accuracy. Additionally, keeping thorough records of income, expenses, and deductions is crucial for a smooth filing experience. Staying informed about updates to tax laws can help you avoid common pitfalls and ensure compliance.
In conclusion, understanding the New York State income tax rate is essential for anyone living, working, or doing business in the state. By familiarizing yourself with the progressive tax system, brackets, and available deductions, you can make informed decisions about your finances. Whether you're a resident, business owner, or non-resident, staying updated on tax laws and regulations will help you navigate the system with confidence. Remember, knowledge is power when it comes to managing your tax obligations effectively.